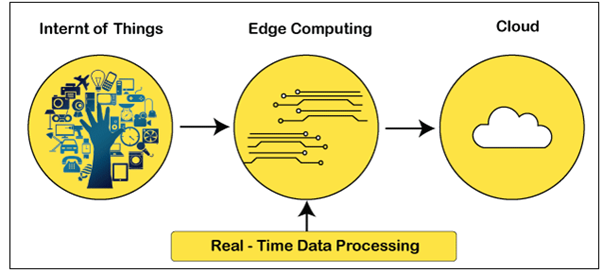
What is Edge Computing
Edge Computing enables the deployment of
computing resources and communication technologies through a unified computing
infrastructure along with the transmission channel.
By using edge computing, computational requirements are more easily fulfilled. Wherever there is an information gathering necessity or where a user performs a specific activity, it can be performed in real-time. Usually, increased efficiency and decreased operational costs are the two primary advantages connected with edge computing, that are defined below.
Advantages of Edge Computing
Some advantages of Edge computing are discussed below-
1. Security
While the emergence of IoT edge computing devices increases the networks'
total attack vectors, it also offers some major safety benefits. The
conventional cloud computing architecture is fundamentally centralized, which
makes it extremely vulnerable to exploitation and power failures from
decentralized denial of service (DDoS).
Edge computing disburses computation, storage, and apps through a broad
variety of devices and cloud services, making it impossible to take down the
service for any single disturbance.
2. Speed
Edge computing's most significant advantage is the potential to improve
network productivity by minimizing the latency. The data they accumulate does
not have to move almost as far as it would under such a conventional cloud
environment, since IoT edge computing devices manage private data or in
neighboring edge data centers.
Speed is completely essential to the business model for many businesses. For
example, the dependence of the finance industry on high-frequency trading
algorithms means that a slowing of simple milliseconds can have serious
impacts. Abandoning a couple of seconds in the healthcare industry may also be
a life or death issue. And for companies that provide consumers with
data-driven utilities, sluggish speeds can annoy consumers and cause of the
long-term harm for a brand.
3. Performance Improvement
Edge computing also collects, analyzes, and conducts appropriate actions on
the gathered data locally, in addition to collecting data for transfer to the
cloud. Although these activities have been completed in milliseconds, no matter
what all the operations might be, it is becoming important to optimize technical
information.
It can be an obstacle to transmit large volumes of data in real-time in a
cost-effective manner, specifically when carried out from isolated industrial
plants. By attaching intelligence to tools available at the network edge, this
issue is resolved. Edge computing takes analytics tools closer to the computer,
which eliminates the middle-man out. This configuration offers less costly
options for maximizing the efficiency of properties.
4. Reducing Operational Costs
Communication, data management, throughput, and performance features are
surprisingly costly in the cloud computing model. Edge computing, which has a
substantially lower bandwidth demand and less bandwidth, remedies this
inefficiency. A useful continuum from the computer to the cloud is produced
through the implementation of edge computing, that can accommodate the vast
amounts of data collected. Expensive bandwidth improvements are no longer
needed, because gigabytes of data need not be transferred to the cloud.
Edge computing may actually reduce cloud reliance and, as a response,
increase the speed of data analysis. In addition, there are also several modern
IoT tools that have sufficient processing power and storage. The transition to
edge computing power enables these devices to be used to their maximum
capabilities.
5. Scalability
The companies can't always predict their IT infrastructure requirements as
businesses expand, and constructing a specialized private cloud is an
unnecessary expense. There is also the problem of tomorrow 's requirements, in
contrast to the considerable up-front building costs and ongoing maintenance.
Conventional private facilities impose an artificial restriction on growth,
locking businesses into predictions of their future computing requirements.
6. Reliability
Related to security benefits gained by edge computing, this should not shock
that it provides better performance. Through IoT edge computing systems and
cloud network infrastructure located directly to end-users, there is less risk
of a network issue in a faraway place impacting local customers. Even in the
case of a local data center failure, since they perform critical processing
capabilities wirelessly, IoT edge computing systems can continue to work
efficiently on their own.
With several network-connected edge computing devices and edge network
infrastructure, any failure to completely closed down service becomes even more
challenging. To help the customers maintain access to the resources and
information they need, information can be redirected across multiple pathways.
Consequently, it can offer unparalleled durability to adopted unanimously IoT
edge computing devices and edge data centers into a detailed edge architecture.
7. Versatility
Edge computing's interoperability also makes it extremely flexible.
Businesses can quickly reach competitive markets without continuing to spend in
costly infrastructure investment by collaborating with local edge data centers.
Edge data centers enable everyone, with little physical constraints or delay,
to serve end-users effectively. For content producers aiming to offer unlimited
subscription services, this is extremely valuable.
Edge computing also makes it possible for IoT systems to collect an important
amount of relevant insights. Edge computing devices are always running, always
linked, and always producing data for future evaluation instead of waiting for
people to log into devices and communicate with hierarchical data centers.
Instances of Edge Computing
The best way to explain the use of Edge computing strategy is through some
instances of edge computing. Here are some circumstances in which the most
efficient is edge computing. They are:
- Broadcasting
Utilities
Some service providers such as Netflix, Hulu, Amazon Prime, and the
forthcoming Disney+ all generate a high network infrastructure load. Through
edge storage, Edge computing creates a great smoother experience. This is when
common data for simpler and faster connectivity is preserved in facilities
closer to end-users.
- Absolutes
vehicles
In order to operate appropriately in real-time, self-driven or Artificial
Intelligence-powered cars and other vehicles need a huge amount of data from
their environment. If cloud storage is being used, a slowdown will arise.
- Intelligent
Homes
The increasing proliferation of smart homes presents a challenge, equivalent
to streaming services. In order to focus on traditional cloud computing only,
it is now much more of network congestion. Processing of data is closer to the
source ensures lower delay in case of an emergency and faster response times.
Medical teams, fire, or the deployment of police are some examples.
If the cloud is placed in different locations around the world, companies
can lose control of their data. For some institutions, such as banks, which are
allowed by law to process information in their native country only, this
configuration may present a problem. Even though attempts are being made to
find a solution cloud computing has obvious drawbacks, when it refers to cloud
data protection.

Comments
Post a Comment